[ By WebUrbanist in Conceptual & Futuristic & Technology. ]
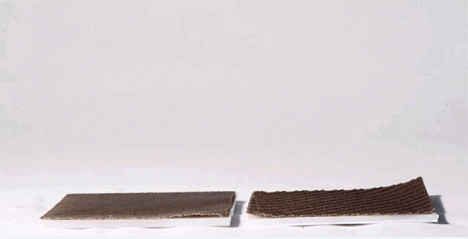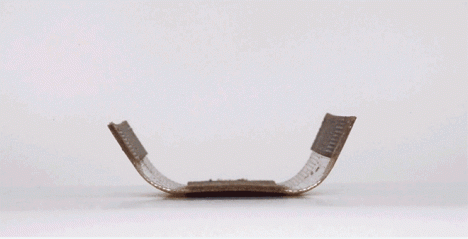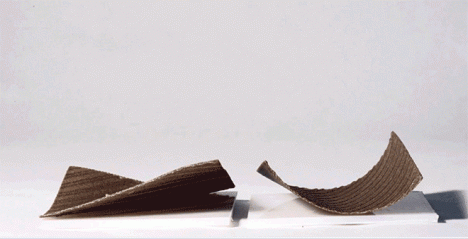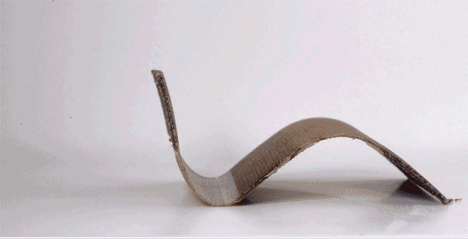
Imagine a shelter that unfolds itself in the rain, flat-pack furniture that deploys without instructions or tools when exposed to water or a temperature-sensitive spoiler for your sports car that bends and twists as you race and turn – thanks to MIT’s Self-Assembly Lab, all of these designs may now be within reach.

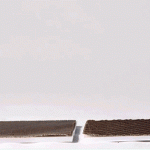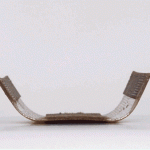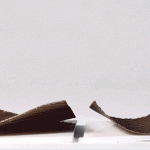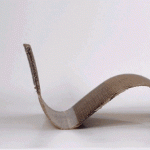
This reactive approach adds a new dimension to objects made of wood, metal, carbon fiber and other materials, each fabricated according to patterns that in turn react to external inputs like low-tech robots. These creations can transform in shape, dynamic and responsive to customizable cues and environmental conditions – heat, cold, dryness and wetness can all be turned into catalysts for a conversion.

Dubbed “four-dimensional printing” by Skylar Tibbits (Research Scientist in MIT’s Department of Architecture) due to the added element of time, this material strategy has proposed applications in various fields ranging from domestic (self-assembling furniture and toys) to vehicular (car spoilers and aircraft wings). Imagine as well, though, apparel that shifts to block rain or allows wind to cool you, or buildings that likewise open to ventilate or let in light and heat based on the weather.

The leap here is as much conceptual and experimental as it is intrinsically revolutionary. As Wired reports, “The tools Tibbits and company use are not especially novel. In the case of the carbon fiber projects, the manufacturing process is thoroughly two-dimensional. The team starts with a carbon fiber roll that follows the typical warp and weft pattern. A secondary material, formulated in Tibbit’s lab to respond to changes in temperature, is spot-printed on the mesh using a CNC gantry. As the carbon fiber is exposed to heat, the temperature-sensitive material changes shape and causes the sheet to deform in ways specified by the designer.”

More on MIT’s Self-Assembly Lab: “Self-Assembly is a process by which disordered parts build an ordered structure through local interaction. We have demonstrated that this phenomenon is scale-independent and can be utilized for self-constructing and manufacturing systems at nearly every scale. We have also identified the key ingredients for self-assembly as a simple set of responsive building blocks, energy and interactions that can be designed within nearly every material and machining process available. Self-assembly promises to enable breakthroughs across every applications of biology, material science, software, robotics, manufacturing, transportation, infrastructure, construction, the arts, and even space exploration. The Self-Assembly Lab is working with academic, commercial, nonprofit, and government partners, collaborators, and sponsors to make our self-assembling future a reality.”






[ By WebUrbanist in Conceptual & Futuristic & Technology. ]
[ WebUrbanist | Archives | Galleries | Privacy | TOS ]

WebUrbanist


























































You must be logged in to post a comment.